How to Set Up a Chess Board
To set up a chess board correctly, place the board so that each player has a white (or light-colored) square in the bottom-right corner. Arrange the pieces on the board with the rooks in the corners, followed by knights, bishops, and then the queen on her color square (white queen on a white square, black queen on a black square). The king stands next to the queen, and the pawns fill the row in front of the main pieces.
Chess Pieces and How They Move
How Does a Rook Move?
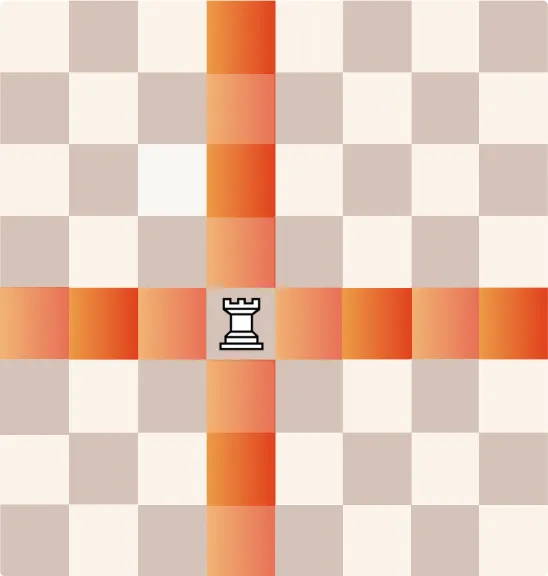
The rook moves in straight lines, either horizontally or vertically, for any number of squares. It’s a powerful piece when used in open lines.
How Does a Bishop Move?
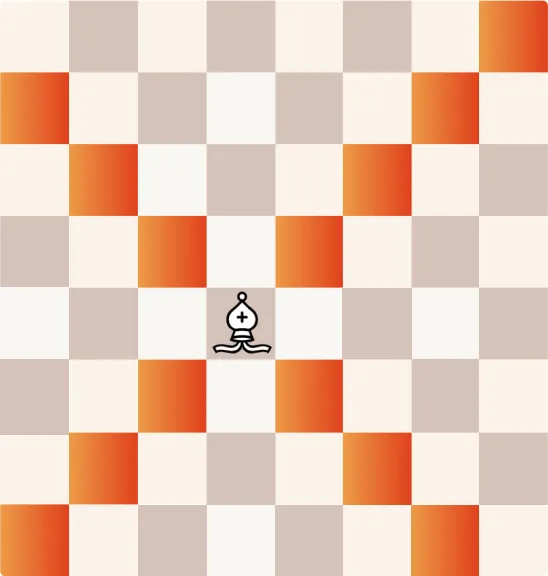

Bishops move diagonally across the board, also for any number of squares. They remain on the same color square throughout the game, so one bishop will stay on light squares, and the other on dark squares.
How Does a Knight Move?
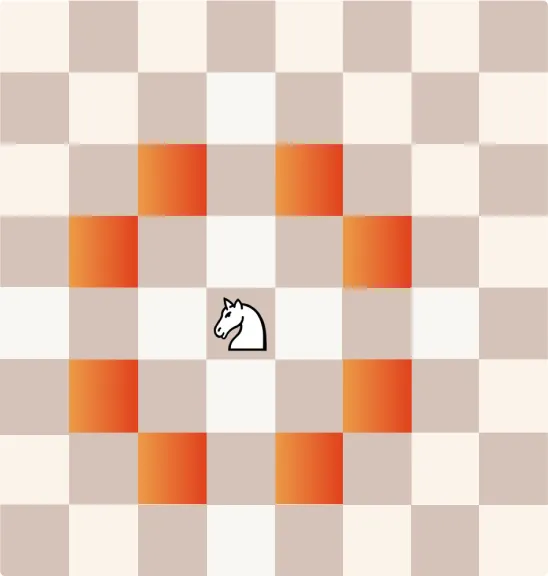
Knights move in an “L” shape: two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular. They are the only pieces that can jump over other pieces, making them especially tricky for opponents.
How Does a Queen Move?
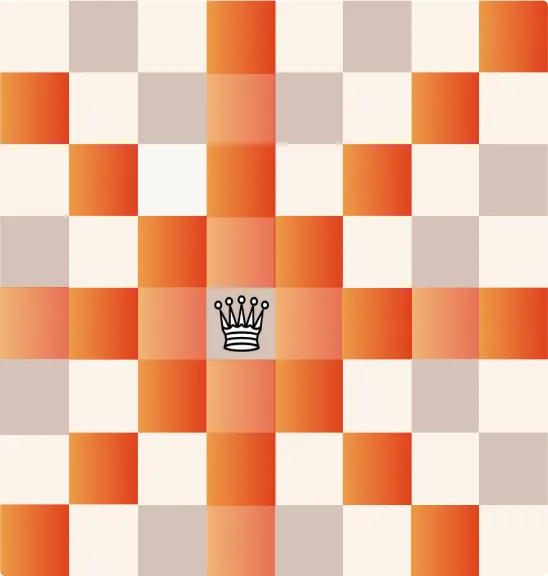

The queen is the most powerful piece in chess, combining the abilities of both the rook and the bishop. It can move horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, making it extremely versatile.
How Does a Pawn Move?
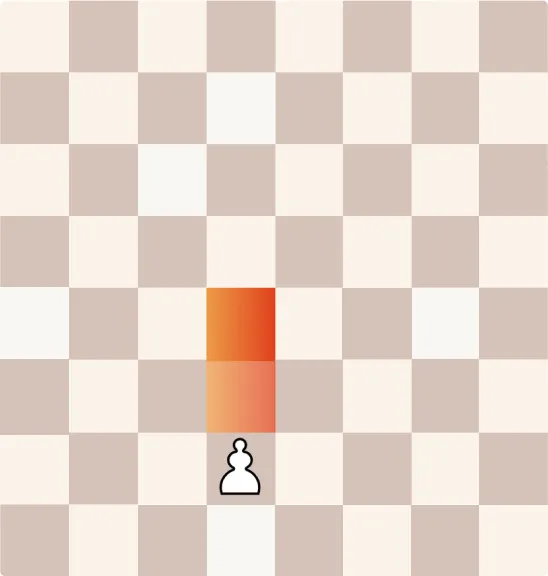

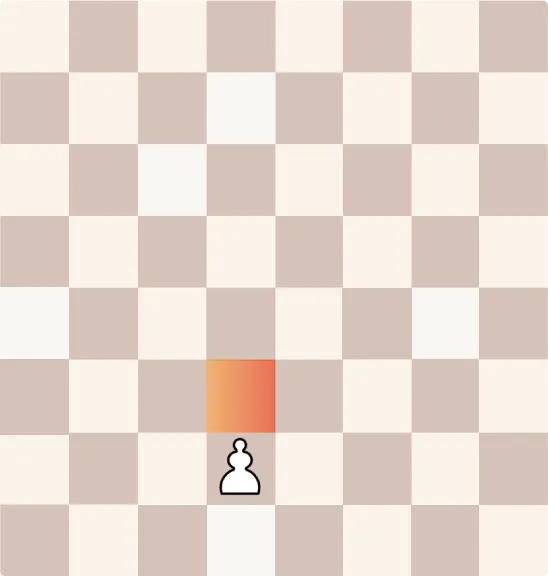
Pawns move forward one square at a time but capture diagonally. On their first move, they have the option to advance two squares.
Pawn Promotion: When a pawn reaches the opponent’s back rank (the eighth rank), it can be promoted to any other piece, usually a queen, giving you a powerful advantage.
Pawn “En Passant”: A special move where a pawn that moves two squares forward from its starting position can be captured as if it had only moved one square. This must be done immediately after the pawn’s two-square move.
How Does a King Move?
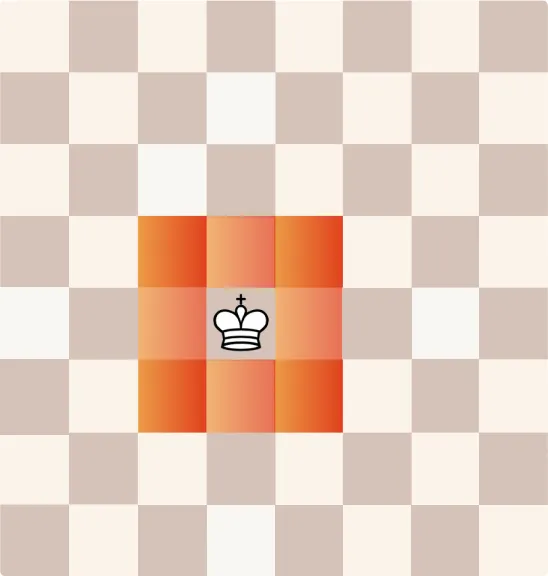
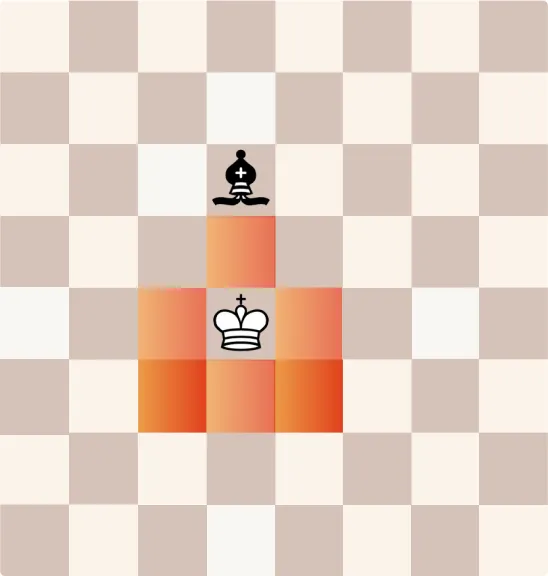


The King moves one square in any direction—horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. Although its movement is limited, the King is essential because losing it results in defeat.
- One square in any direction: The King can move one square at a time in any direction.
- Cannot move into check: The King is prohibited from moving into a square that is attacked by an opponent’s piece.
Castling


Castling is a unique move where the King and one of the Rooks move simultaneously. This special defensive maneuver shifts the King two squares towards a Rook, and the Rook moves next to the King on the opposite side. However, castling is only allowed if:
- Neither the King nor the Rook involved has previously moved.
- The squares between the King and Rook are empty.
- The King is not in check and does not move through or land on an attacked square.
Castling is an essential tactic for safeguarding the King and activating the Rook in the game.
What is Checkmate?
Checkmate occurs when the opponent’s king is in a position to be captured (“in check”) and cannot escape. This ends the game, with the checkmating player declared the winner.
What is Stalemate?
Stalemate happens when a player has no legal moves left but is not in check. The game ends in a draw in this situation.
What is Repetition?
Repetition is a situation where the same position occurs three times in the game, leading to a draw. This can happen when players repeat the same moves without progressing.
With these basic chess rules under your belt, you’re ready to start playing and enjoying the challenge that chess offers.
Any tips for playing better?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a blunder in chess?
What color goes first in chess?
What is Elo in chess?
How many squares in a chess board?
How many pieces in a chess board?
How do chess ratings work?