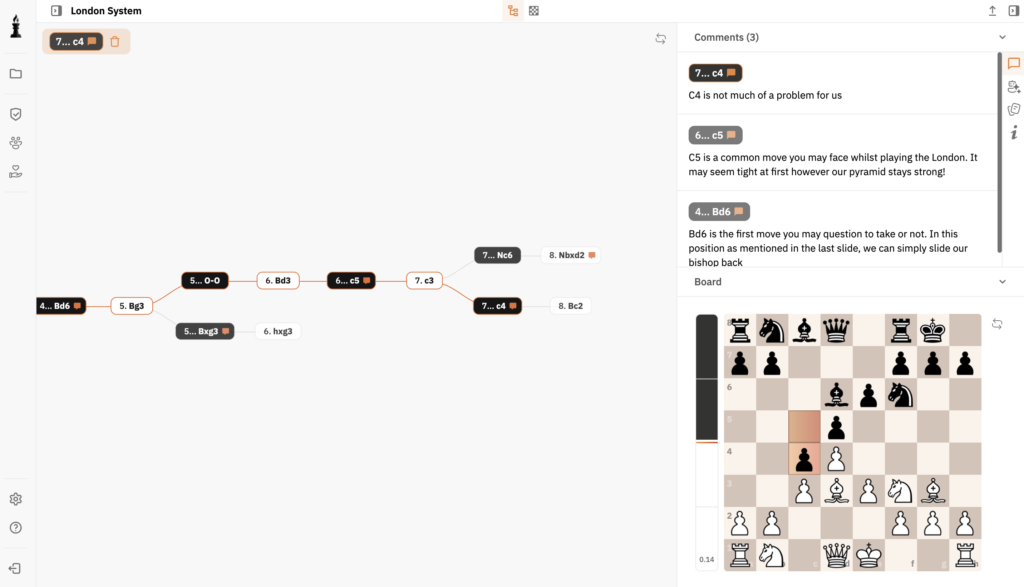
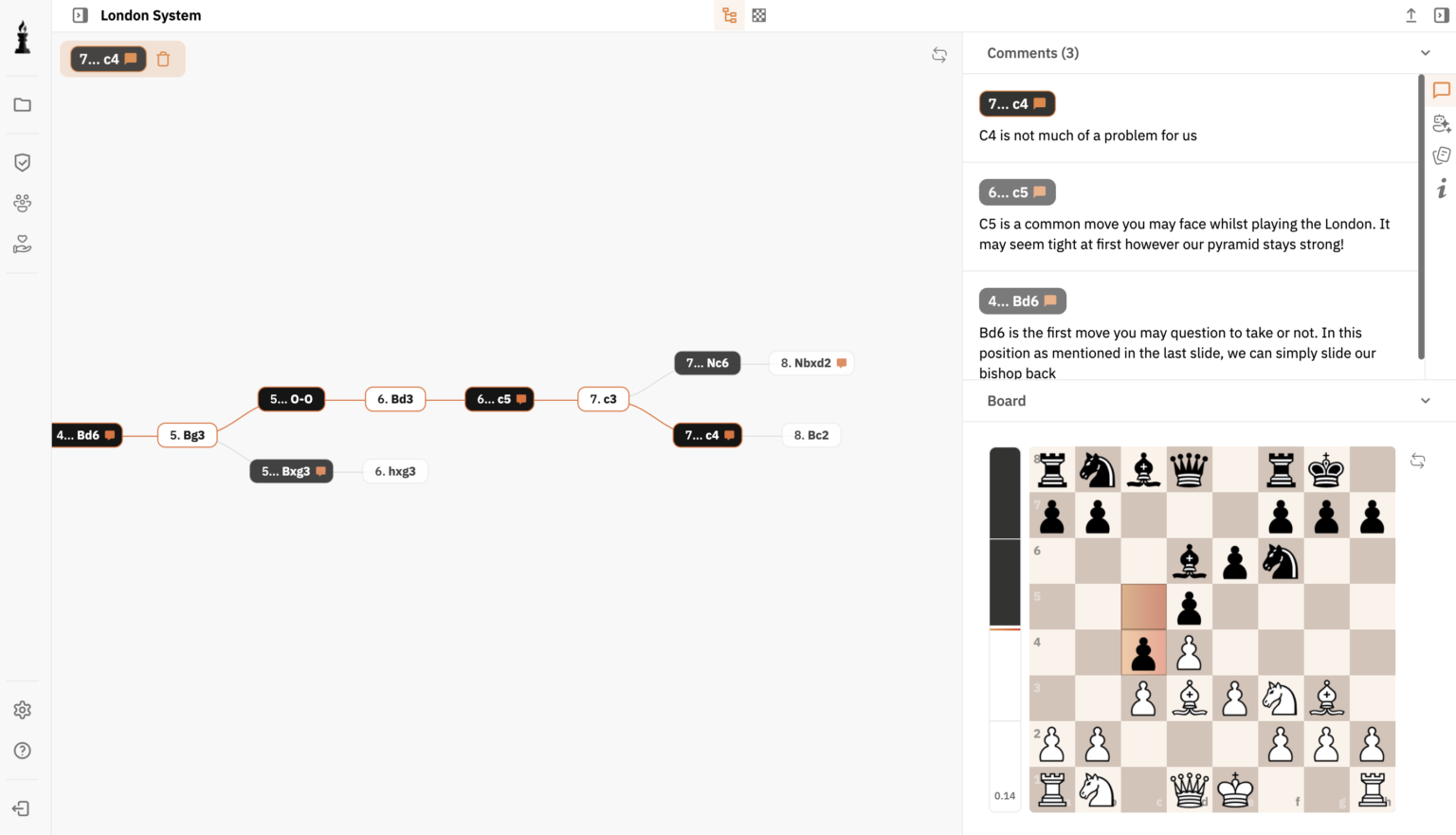
Chess stands as a testament to human intellect and strategy, revered across centuries. A critical period that showcased the transformation of this game was the Renaissance. Chess was not merely a pastime but an essential intellectual pursuit.Italian School highlights a pivotal era.
Rebirth of Thought: Chess in the Renaissance
The Renaissance precipitated a profound shift in how chess was perceived. From a simple board game, it became a subject of study that demanded serious dedication and contemplation. Major players like Francois-André Danican Philidor began to emerge. Philidor’s insight into pawn structures laid modern foundations for strategic planning.
The Italian Renaissance Influence
Italy was a notable chess hub during this time. It produced masters like Gioachino Greco, whose contributions are evident even today. The cunning deployment of pieces and utilization of the fianchetto originated here.
Evolving Strategies and Tactical Innovations
The Renaissance unleashed a plethora of tactical innovations. Concepts like the skewer and pin became better understood. Players such as Philidor devised openings still popular in today’s play.
The Impact of Classical Strategies
Exploring classical strategies by contemporaries like Ruy Lopez and Rudolf Charousek paved exploration in strategies emphasizing controlling the center and tight positional play. Understanding tempo became pivotal. Games weren’t won solely by attacking but by controlling the board rhythm.
The Modern Era’s Chess Evolution
The end of the Renaissance paved the way for a structured evolution, influencing future epochs profoundly. Understanding the opposition, zugzwang, and nuanced exchanges keyed a transition to modern chess planning methods.
Chess in the Enlightenment and Beyond
This period’s forward-thinking enkindled chess waves in Northern Europe. Figures like Johannes Zukertort catalyzed this strategic momentum, leading to structured chess analysis and tournaments.
Chess’s Role: A Tool of Global Strategy
Chess became a metaphor for diplomatic and military strategy through the ages. Even today, players and academics study its principles for insights into human psychology and decision-making frameworks.Stockfish utilizes this, analyzing enormous move databases, blending classical theories with modern computational techniques.
For example, modern thinkers like Bobby Fischer have drawn from deeper theoretical roots. Fischer’s approach, emphasizing foresight and nuanced strategic depth, resembles Renaissance philosophy.
By connecting chess’s historical growth with its present, we appreciate these developments shaping today’s strategies. In recent times, women achieved milestones in chess, with titles like Woman Grandmaster (WGM) and Woman International Master (WIM).
Conclusion
Chess remains a dynamic game, fueled by history yet profoundly influenced by modern thinking. By understanding its Renaissance transformation, one gains a deeper comprehension of chess not just as a game but as a reflection of human strategic perception.
The Renaissance period redefined chess strategy by introducing a deeper analysis of openings and focusing on positional play. Masters like Philidor revolutionized pawn structure theories, while Italian players excelled in tactical innovations such as skewers and pins.
Tempo in chess refers to the pace and momentum of the game. A consistent tempo ensures board control, influencing an opponent’s responses while crafting strategic superiority.
Women have made significant strides in chess, achieving high ranks such as Woman Grandmaster (WGM) and Woman International Master (WIM). They have enriched competitive landscapes with diverse strategic approaches.
Classic tactics like the skewer, pin, and concepts of opposition and zugzwang persist in modern chess. Additionally, strategic planning and tempo from past epochs continue to influence current play.