Chess and Critical Thinking: A Symphony of Intelligence
The game of chess is more than just a pastime; it is a profound exercise in enhancing critical thinking skills. From ancient times to the digital age, chess has been a mirror reflecting the intellectual prowess of its players. This article focuses on how chess cultivates critical thinking, expanding the mind beyond the board.
The Mechanics of Critical Thinking in Chess
Chess requires a player to constantly assess and reassess the status of pieces on the board. Critical thinking begins with recognizing chess patterns. This skill is not only useful in identifying successful strategies but also in adapting to unforeseen circumstances, such as a fork or a skewer.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Chess promotes lateral thinking, a crucial component of problem-solving. Every move in chess demands a decision based on potential risks and benefits. The negotiation between attacking and defending is analogous to resolving complex problems in real life.
Chess Structures and the Cognitive Load
The ability to think several moves ahead defines strategic depth in chess. Concepts like pawn majority and effective pawn promotion teach players to manage resources and plan for the future.
The Role of Chess Tactics
Tactics such as the pin, the double attack, and creating a battery allow players to perform short-term plans within the larger framework of strategy. Successfully employing these tactics requires an in-depth understanding of the position.
How Chess Improves Concentration and Memory
Chess also plays a significant role in enhancing concentration and memory. The mental exercise provided by calculating variations, anticipating zugzwang, or predicting the opponent’s plan is akin to complex mental gymnastics that improve cognitive endurance.
Emotional Intelligence and Chess
Understanding the opponent’s intentions and predicting their moves develops empathy and emotional intelligence. Chess requires understanding both one’s limitations and that of the adversary, leading to growth in self-awareness and regulation.
Integration with Technology
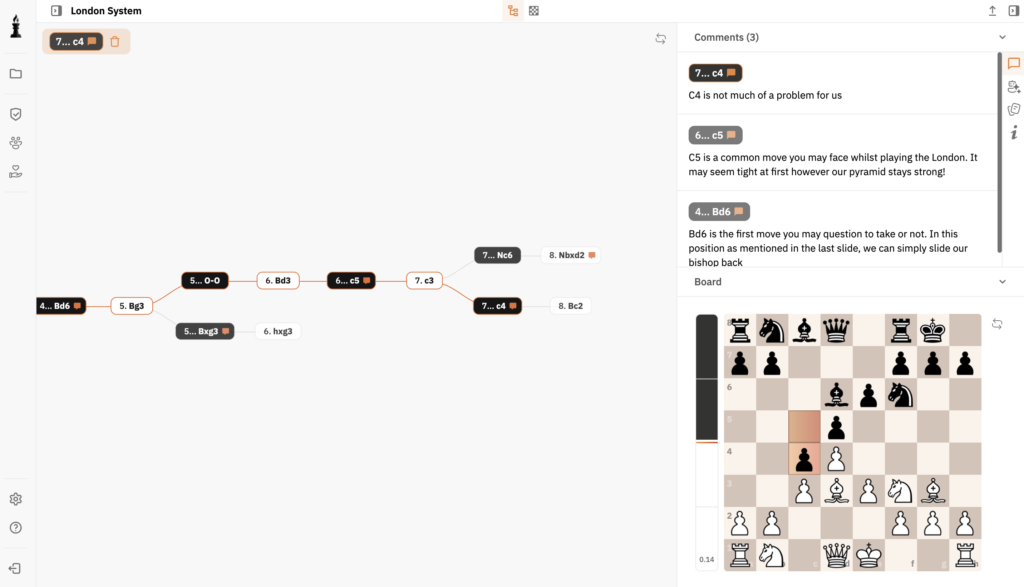
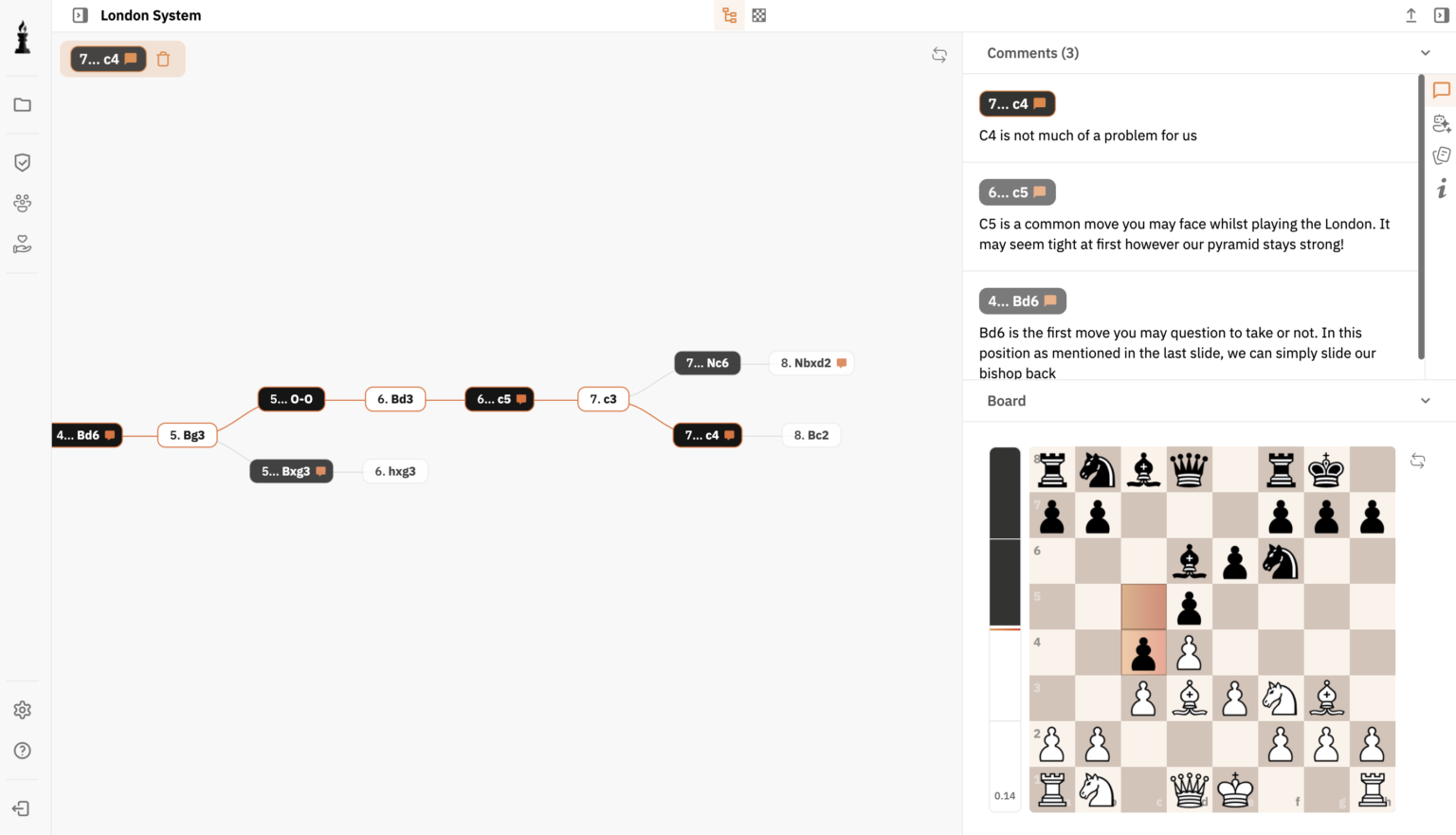
Modern technology enhances the chess experience manifold. Tools like Stockfish provide insights into complex positions and are instrumental in analyzing games. The Chess Games Analysis tool by ChessFlare offers players an opportunity to improve their performance by reviewing and learning from past games.
Conclusion: Beyond the 64 Squares
Chess provides a framework for developing critical thinking and offers lifelong skills that transcend the board’s 64 squares. Whether it’s planning, pattern recognition, or adapting quickly to new situations, the lessons learned through chess are universally applicable.
Ensuring you grow your chess strategies can be eased with tools like the Online Chess Database, where players can expand their knowledge and track progress over time.
Chess remains one of the most robust methods to develop a sophisticated level of critical and strategic thinking that can be effectively applied in real-life scenarios beyond the game itself.
Playing chess enhances problem-solving skills by teaching players to analyze positions, foresee potential outcomes, and make strategic decisions. This process helps develop logical thinking patterns that can be applied in real-world situations.
Chess encourages the use of memory as players need to remember previous moves, recognize patterns, and recall past games to plan future strategies. This constant exercise keeps memory sharp and improves cognitive function.
Yes, chess helps improve emotional intelligence by requiring players to anticipate opponents’ moves, understand their strategies, and manage emotions under pressure. This interaction increases empathy and self-regulation.
Technology plays a crucial role in modern chess learning by providing analysis tools like Stockfish, facilitating the review of games, and offering platforms for learning techniques. Applications and databases help players expand their understanding efficiently.